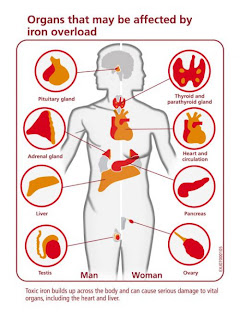
Iron supplements are commonly used to treat anemia. Iron can also be found in most multivitamin supplements. People, including small children can overdose on the pills, causing iron poisoning. Because many people take multivitamin supplements, iron poisoning is a common occurrence. Children's vitamin supplements do contain iron, but usually not enough to cause serious poisoning. Overdose of pure iron supplements, however, may cause serious iron poisoning. Iron poisoning occurs when a person, usually a child, swallows a large number of iron-containing pills, most often vitamins. Acute iron poisoning mainly involves children younger than 6 years who swallow pediatric or adult vitamins containing iron. These children may not be able or willing to tell you what and how much they swallowed. Iron salt is available in multiple preparations. For instance, ferrous sulfate is available as drops, syrup, elixir, capsules, and tablets. Iron preparations are widely used and are available without a prescription and may be housed in bottles with or without child resistant closures. The amount of iron that will cause poisoning depends upon the size of the child. An 8-year-old may show no symptoms from an amount that would cause serious symptoms in a 3-year-old. Symptoms appear at doses greater than 10 mg/kg (based on the body weight of the child). Iron is available in different oral forms. A child may show no symptoms after eating a number of pills that might have looked like candy. The only evidence may be an opened vitamin bottle. If you know, or even suspect, that a child has eaten tablets, you should consult a hospital’s emergency department or a poison control center regarding a possible iron poisoning.
Symptoms
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Abdominal Pain
Drowsiness
Unconsciousness
Seizures
Stomach bleeding (with serious poisoning)
Rapid heart rate (with serious poisoning)
Low blood pressure (with serious poisoning)
Diarrhea
Abdominal Pain
Drowsiness
Unconsciousness
Seizures
Stomach bleeding (with serious poisoning)
Rapid heart rate (with serious poisoning)
Low blood pressure (with serious poisoning)
Very low blood pressure (shock)
Bleeding
Jaundice
Liver failure
Seizures
Confusion
Decreased blood sugar
Coma
Bleeding
Jaundice
Liver failure
Seizures
Confusion
Decreased blood sugar
Coma
Treatment
Iron poisoning is diagnosed based on the history of the person’s history, symptoms, and the amount of iron found in the blood. If an excessive amount of pills have been swallowed, they can sometimes be seen in the stomach in an x-ray. In the case of serious iron poisoning, the person will need to be hospitalized. Injections of deferoxamine, which binds iron the blood, are given.
More Details
www.rightdiagnosis.com
www.emedicinehealth.com